A farmer-centric low emission rice program
Sustainable Paddy (SuPad) Initiative
Why sustainable rice cultivation matters
Rice cultivation is critical for India, covering over 46 million hectares (28% of global rice acreage) and sustaining millions of smallholder livelihoods. However, current practices present major challenges:
-
Flooded paddy systems are among the largest agricultural sources of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, responsible for 18–20% of India’s agricultural emissions, primarily methane and nitrous oxide. Improved water management is a key pathway to slow and mitigate global warming.
-
Continuous flooding leads to excessive water use and severe groundwater depletion.
-
Current carbon markets are often driven by flawed, profit-driven models. Farmers—the actual generators of emission reductions—are often severely undercompensated, receiving as little as 10–20% of carbon revenue, with most benefits going to intermediaries.
The Solution
Farmer-centric, measurement informed initiative
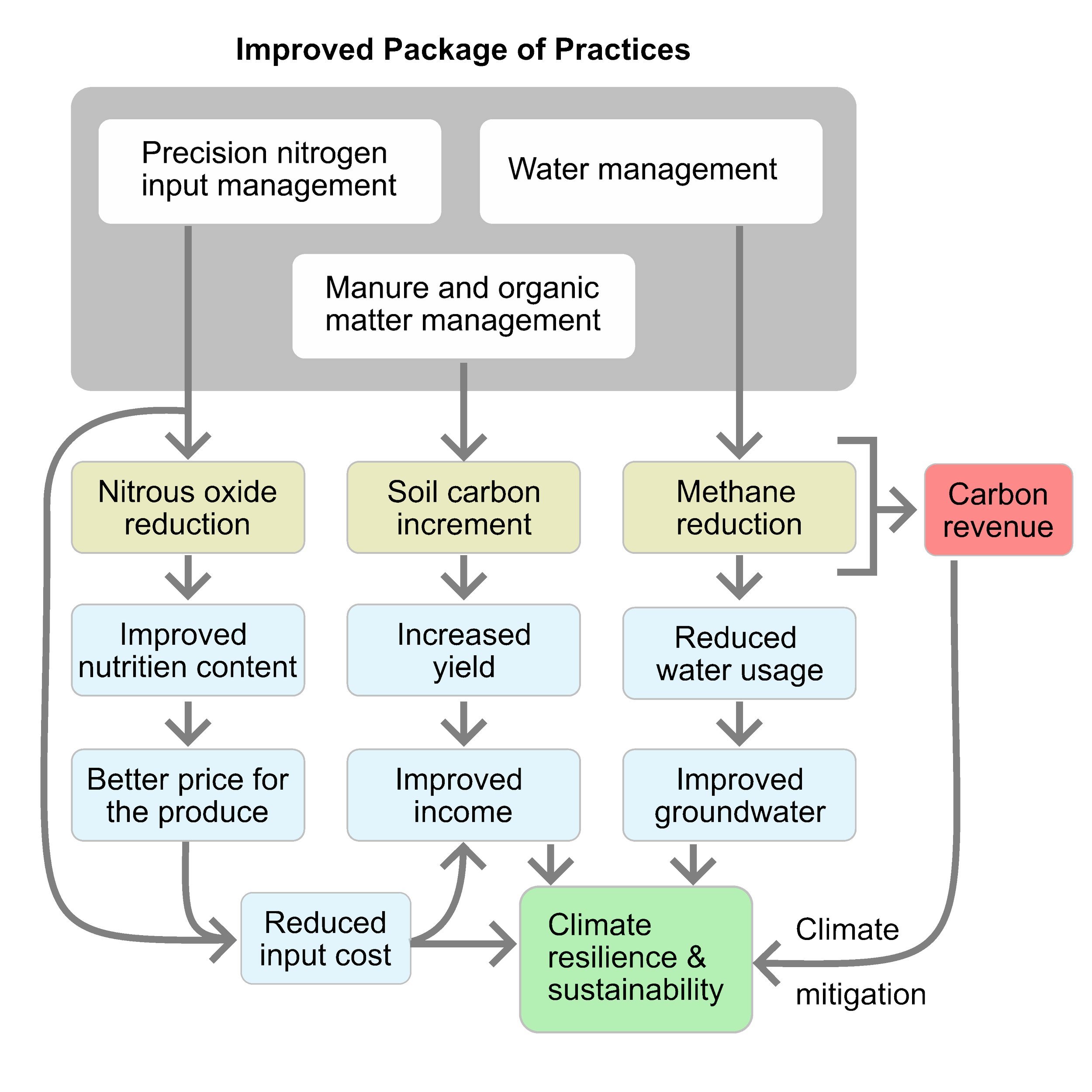
The SuPad Initiative introduces a rigorous, measurement-first, farmer-led model designed to achieve credible GHG reductions, ensure stable yields, and provide equitable returns. SuPad combines advanced techniques to enhance water conservation, soil health, and precision agriculture.
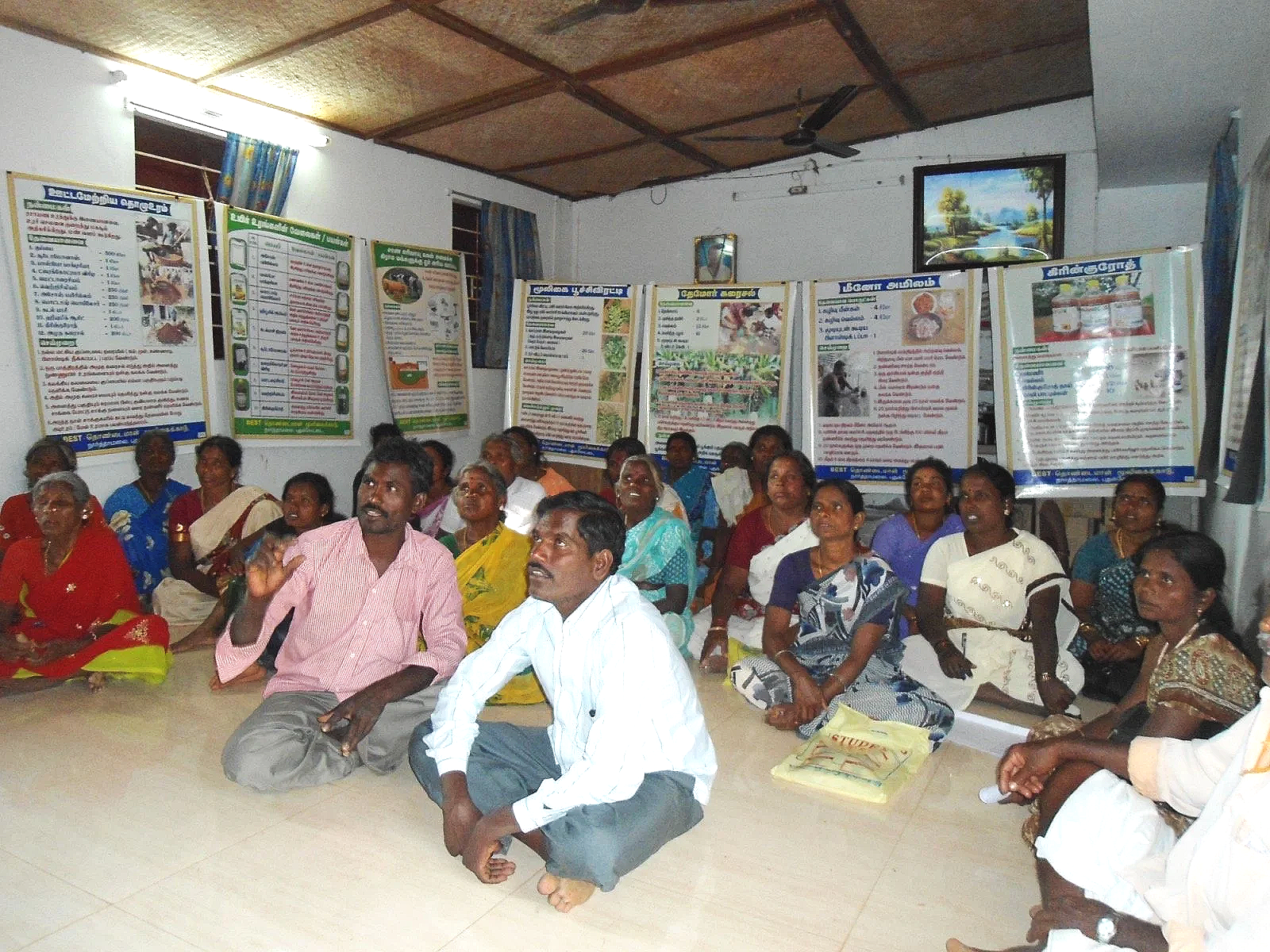
The practices we promote on farmers’ plots are regionally tested, proven by lead farmers to lead to better yields. We do not compromise on farmers’ returns.
-
The model integrates cutting-edge AWD with precision irrigation and fertigation systems.
-
The climate-smart sustainable package of practices (PoPs) is developed bottom-up, ensuring they are long-tested and demonstrate yield benefits before being promoted. This umbrella approach includes improved water management, optimal nutrient management (specifically for nitrogen inputs), residue management, and natural pest control techniques.
-
The solution ensures credible reductions in both methane and nitrous oxide. SuPad uses patent-pending measurement systems fully aligned with Verra VM0051—the most rigorous methodology available that emphasizes empirical measurement.
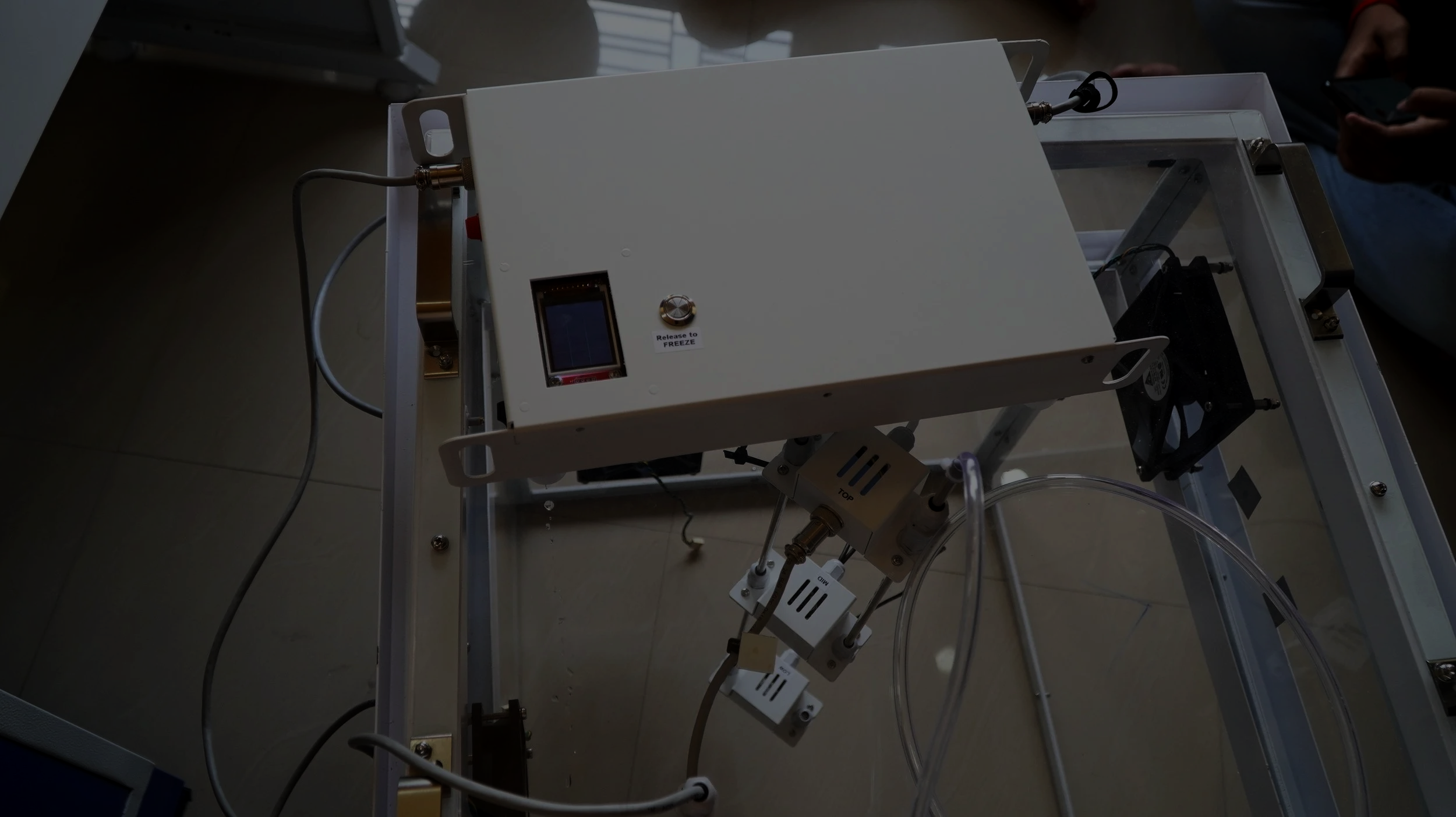
Measurement & verification rigour
SuPad implements a measurement-first approach, ensuring emission reductions are quantified upfront to build financial models with confidence.
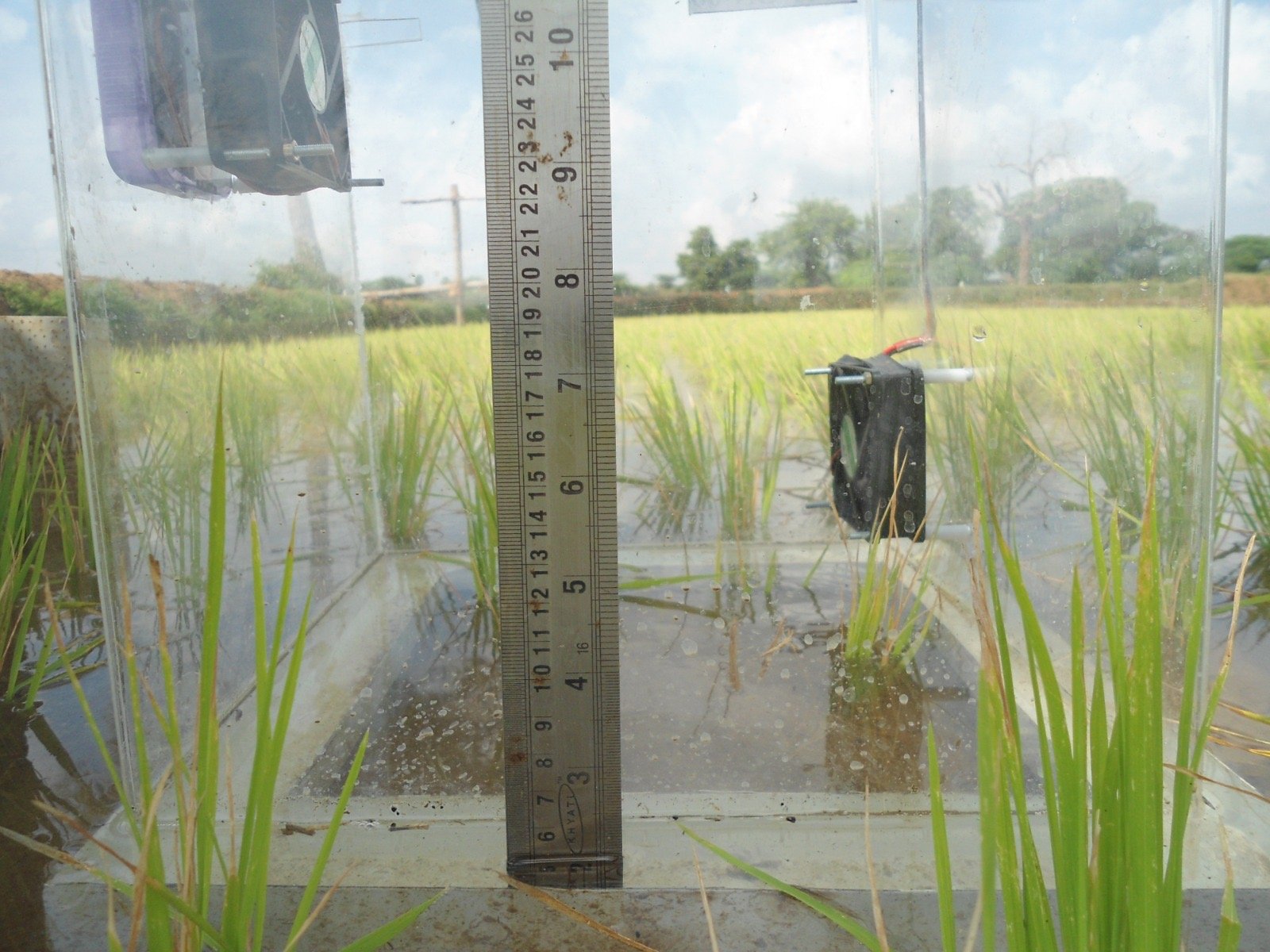
Empirical Data: State-of-the-art trace gas monitoring laboratories are established in the project area to accurately sample methane and nitrous oxide emissions from reference plots.
Digital MRV (DMRV): Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification systems utilize Satellite data (ISRO–NASA NISAR) combined with Internet of Things (IoT)-based validation for transparent digital monitoring. The project is also developing its own home-built database solution to make monitoring financially viable and transparent.
Impact and farmer returns
SuPad is designed to empower farmers and enhance India’s leadership in climate-smart agriculture.
Equitable Sharing: 60–70% of the carbon revenue flows directly to the farmers, serving as a supplementary income stream.
Viable Returns: Focusing on area with maximum emission reduction potential, we ensure that a credible and scalable rice GHG mitigation project can fetch better price for the carbon - thus enabling adoption by farmers.
Enhanced Livelihoods: The project aims to improve farm income through direct commodity trading, supply chain optimization, and value-added products (like rice bran oil and rice husk-based products).

Source rice grown sustainably to enrich soil and boost nutrient quality — offering better grains for your customers and a healthier planet.
The initiative is led by scientists who developed the rice carbon emission protocols and is backed by a large grassroots consortium of 70+ NGOs with two decades of experience.